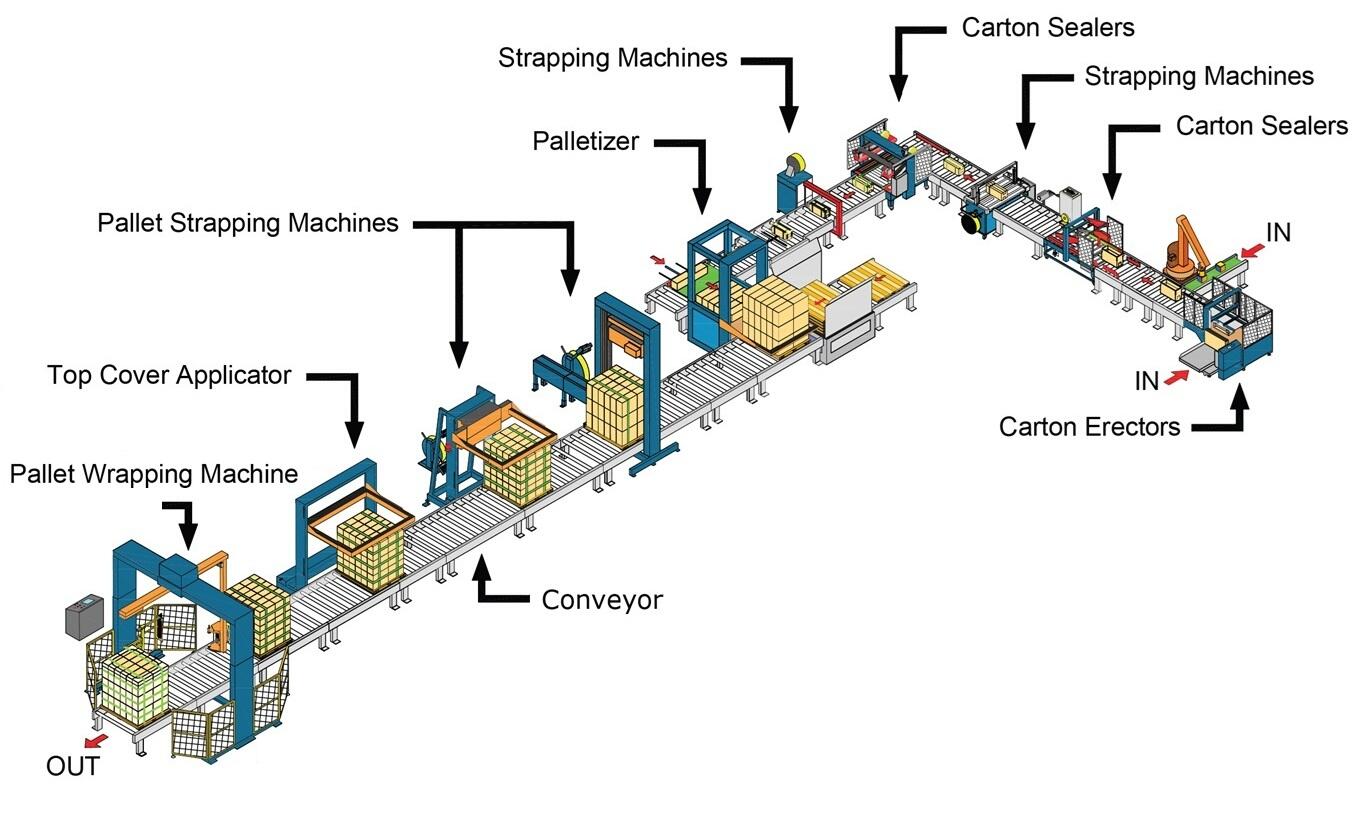
Understanding Strapping Machines: How They Work
- What Is a Strapping Machine
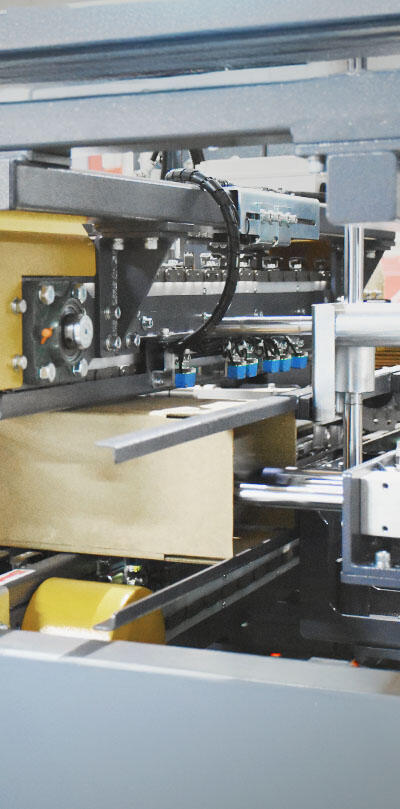
- Main Components of a Strapping Machine
- Different Types of Strapping Machines
- How Does a Strapping Machine Work
- Common Applications of Strapping Machines
- Maintenance Guidelines for Strapping Machines
- FAQ About Strapping Machines
- Optimize Packaging Performance with Strapping Machines

Strapping is a crucial step in securing packages, ensuring stability and protection during storage and transportation. Integrating a strapping machine into your packaging line improves operational efficiency and guarantees consistent, reliable results.
This guide provides a complete overview of strapping machines—what they are, how a strapping machine works, their components, types, applications, and essential maintenance practices.
What Is a Strapping Machine
A strapping machine is a packaging machine that uses durable straps, usually made of plastic (PP or PET) or steel, to tightly bundle or secure cartons, pallets, or other items. The purpose of strapping is to keep goods firmly fixed in place, preventing damage or shifting during storage and transportation.
Strapping machines are widely adopted across industries because they enhance package security, streamline production, and significantly reduce manual labor costs.
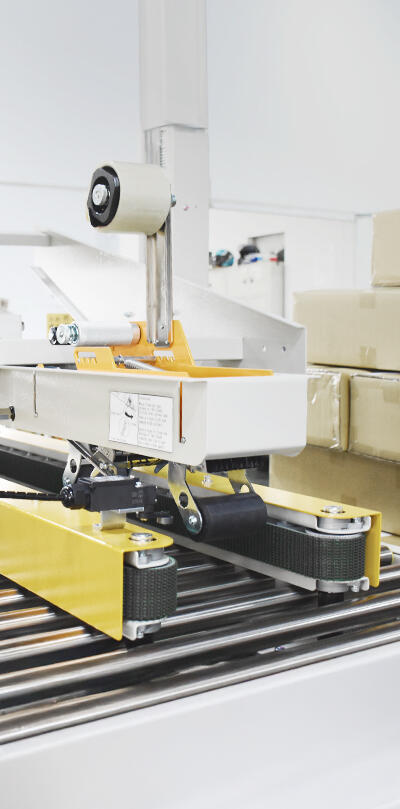
Main Components of a Strapping Machine
Key components include:
- Frame: Provides structural support, including a worktop where packages are positioned for strapping.
- Strap Dispenser: Stores and feeds the strap roll into the machine.
- Strap Guide Rail: Directs the strap along a fixed path for accurate positioning.
- Strap Feeding System: Releases and retracts the strap, moving it smoothly through the guide rail and into the correct position.
- Tensioning System: Tightens the strap using an electric motor or pneumatic device. The tension level can be adjusted for different applications.
- Sealing System: Bonds the strap ends together to secure the object. Common methods include heat sealing, friction welding, ultrasonic welding, and metal seals.
- Cutter: Cuts off excess strap after sealing.
- Control System: Manages machine operations. Manual machines rely on buttons or foot pedals, while semi-automatic and fully automatic models use PLC-based control panels.
- Power System: Provides the driving force, typically through electric motors, for feeding, tightening, and sealing the straps.
- Safety Features: Includes emergency stops, overload protection, and guards for safe operation..
- Optional Auxiliary Components:
- Conveyor: Transport packages in and out of fully automated systems.
- Adjustable Height Stands: Enable the machine to align with the height of other equipment for smooth integration.
- Cooling System: Found in heat-sealing models to shorten cycle time and ensure firm seals.
Different Types of Strapping Machines
The most common way to categorize strapping machines is by their level of automation:
Manual Strapping Machines
These machines rely entirely on manual operation without electricity. They are usually portable, lightweight, and easy to use. Ideal for small-scale workflows, temporary setups, or outdoor use where flexibility and budget considerations are important.
Semi-automatic Strapping Machines
Operators place packages manually and activate the machine via foot pedals or buttons. The machine then feeds, tensions, seals, and cuts the strap automatically. Semi-automatic models are suitable for small to medium businesses, offering efficiency and affordability.
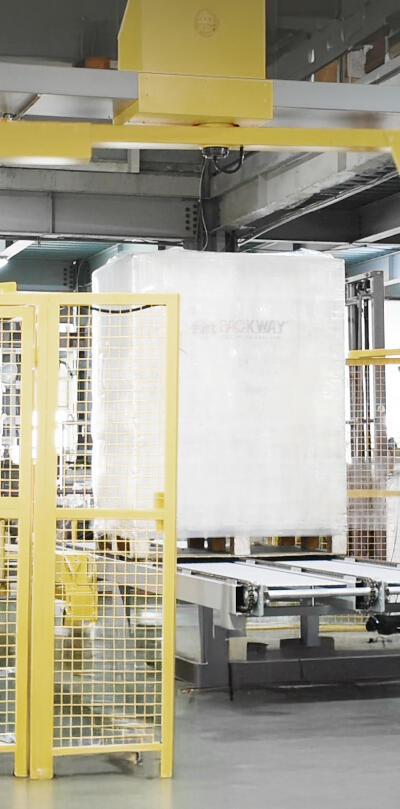
Fully Automatic Strapping Machines
These machines complete the strapping process without manual intervention. Integrated with conveyors, sensors, and PLC controls, they are ideal for large-scale production in factories or logistics centers. They offer high efficiency and labor savings but require higher initial investment and regular maintenance.
How Does a Strapping Machine Work
While different types of strapping machines may vary in details, their workflow can generally be divided into two main stages: setup and operation.
Setup Process
Installing the strap
Load the strap roll into the strap dispenser, ensuring it follows the correct feeding direction. Then, thread the strap through the guide rail and the feeding system until it reaches the sealing position.
Setting Parameters on the Control Panel
Adjust the strap tension level, sealing method, sealing time, cycle mode, and other parameters depending on the machine type.
Operation Process
Loading the Package
For semi-automatic machines, the operator positions the package manually. Fully automatic machines use conveyors to place packages correctly in the production line.
Strap Feeding
The strap is released from the dispenser and guided through the strap guide rail to wrap around the package, either manually using foot pedals or buttons, or automatically.
Strap Positioning
The feeding system ensures the strap is accurately positioned across the sealing area and then automatically or manually stops feeding.
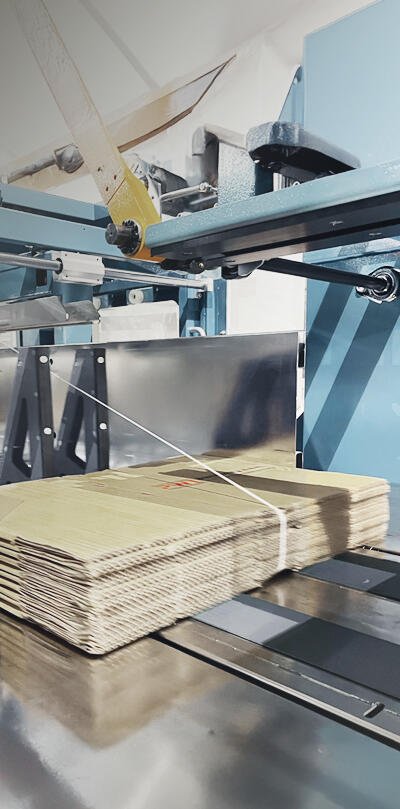
Tensioning
The tensioning system tightens the strap around the package. The tension level can be adjusted depending on the package type and required firmness.
Sealing
The sealing system bonds the strap ends together. Common sealing methods include heat sealing, friction welding, ultrasonic welding, or metal seals.
Cutting
The cutter removes excess strap, leaving the package securely strapped.
Completion & Next Cycle
Once strapping is completed, the package is either removed manually or conveyed forward, and the machine resets for the next cycle.
Common Applications of Strapping Machines
Used across multiple industries, strapping machines help stabilize packages and protect their contents during transit. Common uses include:
- Logistics & Warehousing: Bundling cartons, pallets, and bulk goods for safe storage and transportation.
- E-commerce & Retail Distribution: Securing parcels and mixed shipments to improve efficiency and protect products during last-mile delivery.
- Electronics Industry: Strapping cartons of computers, mobile devices, appliances, and electronic components to prevent movement or damage in transit.
- Food & Beverage Industry: Bundling bottled drinks, canned goods, packaged foods, or bulk boxes for stable handling and distribution.
- Building Materials & Construction: Securing heavy or irregular-shaped items such as bricks, tiles, steel rods, and wooden planks.
- Automotive & Industrial Products: Packaging spare parts, machinery, and tools to ensure stability in shipping and warehouse handling.
- Printing & Publishing: Strapping stacks of newspapers, magazines, books, or printed materials for organized and easy distribution.
Maintenance Guidelines for Strapping Machines
Regular maintenance prolongs machine lifespan and ensures consistent strapping quality. Maintain reliable operation by:
- Clean surface, guide rails, and sealing area daily.
- Check strap quality, dispenser setup, and power supply.
- Inspect and lubricate feeding, tensioning, sealing, and cutting systems regularly.
- Avoid overload, keep the environment dry, and monitor sensors.
- Perform daily, monthly, and yearly checks, and call professionals when necessary.
FAQ About Strapping Machines
Q1: How to Choose the Right Strapping Machine?
- Manual: Small-scale or mobile use with low volume.
- Semi-automatic: Small and medium-sized enterprises with moderate volumes, offering a balance of cost and efficiency.
- Fully automatic: High-volume factories or logistics centers requiring production line integration.
Q2: Which Strapping Material Should I Use?
- PP Straps: Low cost, suitable for light packages.
- PET Straps: Stronger, ideal for medium to heavy loads.
- Steel Straps: Maximum strength for very heavy or high-value items; requires safety precautions.
Q3: What About Maintenance Costs and Lifespan?
A: Manual tools require minimal maintenance and can last over ten years. Semi-automatic machines need periodic replacement of consumables and typically last 5–10 years. Fully automatic models have higher maintenance needs but, with proper care, can operate reliably for 5–15 years. Regular cleaning, lubrication, and preventive checks are essential. Proper maintenance not only extends machine life but also prevents costly downtime and ensures consistent strapping quality.
Optimize Packaging Performance with Strapping Machines

Packaging is only complete when products reach customers safely and without damage. Strapping reinforces package integrity, and selecting the right strapping machine helps streamline operations while ensuring every shipment is securely protected.
PACKWAY offers a full range of solutions from semi-automatic to fully automatic machines, supported by expert guidance for selection, installation, and after-sales service.
Contact us today to explore the ideal strapping solution for your business and elevate your packaging performance.